Now translated into Chinese for 原文来自于OrthoStreams here

COVID has accelerated change everywhere. Some sectors are being turned upside down – retail shops, restaurants, tourism, travel, leisure, education, casinos, live entertainment, sporting events, etc. Ultimately, fifty million Americans will find new ways to earn a living.
Fortunately for the orthopedics device community, orthopedic care is still in huge demand. Elective surgeries are being resumed mid-year.
However, the Orthopedics Industry is going through a metamorphosis. The Great Reset. I call this new phase Orthopedics 3.0.
First let me walk you through some quick history of major shifts in orthopedics 1.0 and 2.0, then I will introduce 3.0.
Orthopedic care has been around a long time. Fracture repair began in the middle ages including the use of casts and crutches. I peg the beginning of modern orthopedics around 1960 with the advent of OA treatment and the the first protheses.
Orthopedics 1.0
Orthopedics 1.0 was conceived with a focus on PAIN RELEIF.
In 1960, Sir John Charley ushered in “low friction arthroplasty” with stainless steel and teflon (later changed to polyethylene). Charley implanted the first stainless steel monoblock hip stems with PMMA and polyethylene cups in the 1960s. The Charley Hip was available in one size.
Dr. Marmor brought the first total knees to the world in the 1970s with three sizes. Marmor implanted side by side unis to create the first total knee.

Very few materials and few sizes were available. No rights or lefts. The surgeon had to make the implant fit the patient. Sounds barbaric, but that’s the way it was.
During Orthopedics 1.0 device companies concentrated on improved materials, kinematics and bone conservation. The FDA started regulating orthopedic devices in 1976.
Orthopedics 2.0
Orthopedics 2.0 was born with a focus on SURGICAL OPTIONALITY. This started aronud 1980 with the surgeon’s insatiable need for more choice – more anatomic sizes, lefts/rights, technology, constraints, surgical approaches, MIS, etc. Device companies like Biomet started making customs for each surgeon in the 1980s.
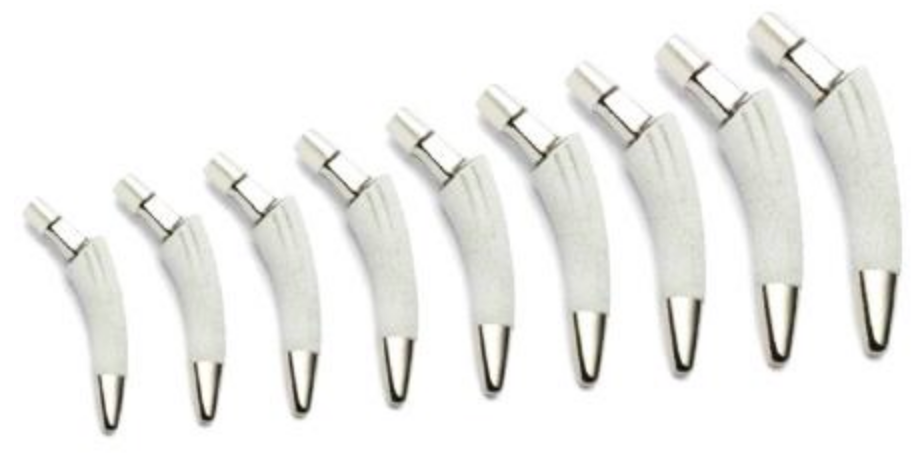

The more implant choices the better. Choice became an addictive. The surgeon demanded every possible implant and instrumentation option in surgery to provide the best treatment for the patient.
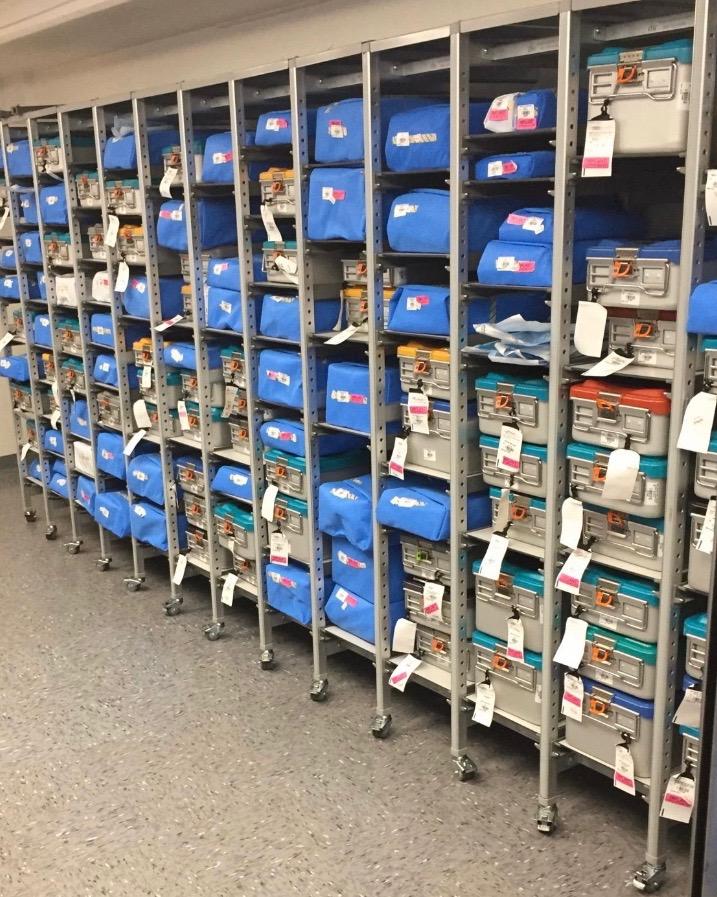

A new crop of practicing surgeons were trained on optionality and became hooked on optionality. Device companies were happy to deliver more choices.
The result of the 2.0 focus was increased procedure complexity, increased product available for each case and higher costs.
Orthopedics 3.0
In 2020, we transitioned to Orthopedics 3.0. The new focus is AUTOMATION. This is driven by the need for less human touch, greater efficiencies and less burden on hospitals. Ortho 3.0 is focused on all processes that touch the healthcare system; whereas, Ortho 2.0 was primarily focused on the surgical event. From the device company point-of-view, this new metamorphosis effects R&D, testing, marketing, surgical training, Med Ed, clinical studies, finance, operations, selling, marketing, service, inventory, and logistics.


 The Orthopedics Industry
The Orthopedics Industry